In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. One of the fundamental aspects that can make or break your online presence is indexing. Proper indexing ensures that your website gets noticed by search engines, which in turn helps potential customers find you. This blog will delve into the intricacies of indexing, its significance in digital marketing, and how you can optimize your website to achieve better indexing.
Indexing is a fundamental aspect of Digital Marketing that directly impacts your online visibility, traffic, and overall success. By understanding the intricacies of indexing and implementing effective strategies to optimize your website for search engine crawlers, you can ensure that your digital content is discoverable and accessible to your target audience.
What is Indexing in Digital Marketing?

Indexing in digital marketing refers to the process by which search engines organize and store the information they gather from websites. When search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo crawl the web, they collect data from various web pages and add it to their index, which is essentially a giant database of all the content they have discovered. This indexed data is what search engines use to provide relevant results to users when they search for specific keywords or phrases.
Why is Indexing Important?
Indexing is crucial for several reasons:
- Visibility: If your web pages are not indexed, they will not appear in search engine results pages (SERPs), making it difficult for potential customers to find you.
- SEO: Proper indexing is a foundational element of search engine optimization (SEO). It ensures that search engines can easily find, understand, and rank your content.
- Traffic: Indexed pages are more likely to drive organic traffic to your site, as they can be found by users searching for relevant topics.
- User Experience: Proper indexing ensures that users can quickly find the information they are looking for, improving their overall experience on your site.
How Indexing Works
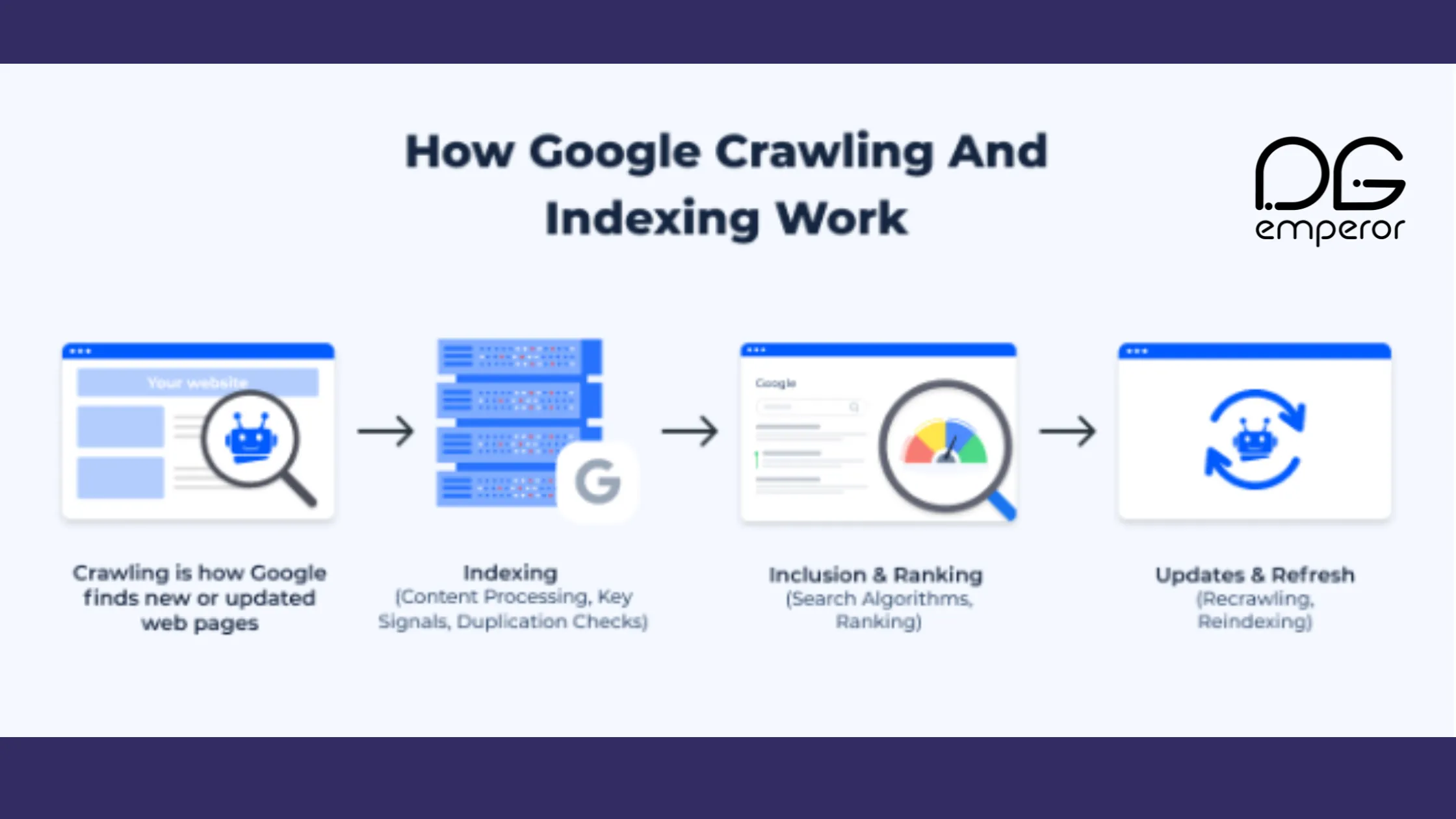
The indexing process involves several steps:
- Crawling: Search engines use bots (also known as spiders or crawlers) to explore the internet and discover new and updated content. These bots follow links from one page to another, gathering information along the way.
- Processing: The data collected by the crawlers is then processed. This involves analyzing the content, images, and meta tags to understand what each page is about.
- Storing: The processed information is stored in the search engine’s index. This index is a massive database that contains all the web pages the search engine has discovered and analyzed.
- Ranking: When a user enters a search query, the search engine retrieves relevant results from its index and ranks them based on various factors such as relevance, quality, and user experience.
Factors Affecting Indexing
Several factors can influence how well your web pages are indexed:
- Website Structure: A clear and logical structure helps search engines crawl and index your pages more efficiently. Organize your content with categories and subcategories.
- Internal Linking: Effective internal linking allows search engines to discover new pages on your site. Ensure that all important pages are linked from other relevant pages.
- Sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website. Submitting a sitemap to search engines can improve crawling and indexing.
- Robots.txt: This file tells search engines which pages they can and cannot crawl. Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to avoid blocking important pages.
- Meta Tags: Meta tags, such as title tags and meta descriptions, provide information about your pages to search engines. Use relevant keywords and write clear, descriptive meta tags.
- Content Quality: High-quality, original content is more likely to be indexed and ranked well. Avoid duplicate content, which can harm your indexing and rankings.
How to Ensure Your Website is Properly Indexed
To ensure your website is properly indexed, follow these actionable tips:
1. Create a Sitemap
A sitemap is a blueprint of your website that helps search engines find and index your pages. You can create a sitemap manually or use tools like XML Sitemap Generator. Once created, submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
2. Optimize Your Robots.txt File
Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow search engines to crawl your important pages. Avoid disallowing pages that you want to be indexed.
3. Use Internal Links Strategically
Link to important pages from other relevant pages within your site. This helps search engines discover and index new content.
4. Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. Ensure your website is mobile-friendly to improve indexing.
5. Fix Crawl Errors
Regularly check for crawl errors in Google Search Console. Fixing these errors ensures that search engines can access and index your pages without issues.
6. Update Content Regularly
Regularly updating your content keeps it fresh and relevant. Search engines favor updated content, which can improve your indexing and rankings.
7. Use Structured Data
Implementing structured data (schema markup) helps search engines understand your content better, leading to improved indexing and richer search results.
8. Avoid Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and harm your indexing and rankings. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page when necessary.
Common Indexing Issues and How to Resolve Them

Even with the best practices, you might encounter some common indexing issues. Here’s how to address them:
1. Pages Not Indexed
If some of your pages are not indexed, check your robots.txt file and meta tags to ensure they are not blocking these pages. Also, verify that the pages are linked from other parts of your site.
2. Slow Crawling
If search engines are crawling your site slowly, it might be due to server issues or a lack of internal links. Improve your site’s performance and ensure all pages are well-linked.
3. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can lead to indexing issues. Use tools like Copyscape to check for duplicates and use canonical tags to specify the original version of the content.
4. Incorrect URL Parameters
URL parameters can cause indexing issues if not managed properly. Use Google Search Console to specify how URL parameters should be handled.
Tools to Help with Indexing
Several tools can help you manage and monitor your website’s indexing:
- Google Search Console: This free tool provides insights into how Google is indexing your site and highlights any issues that need attention.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Similar to Google Search Console, this tool provides insights and diagnostics for Bing’s indexing of your site.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: This tool crawls your site like a search engine, providing detailed reports on your site’s structure, links, and indexing status.
- XML Sitemap Generators: Tools like XML Sitemap Generator help you create and manage sitemaps for your website.
- Copyscape: Use this tool to check for duplicate content and ensure your pages are unique.
Advanced Indexing Techniques
For those looking to delve deeper into indexing, here are some advanced techniques:
1. Log File Analysis
Analyze your server log files to understand how search engines are crawling your site. This can help identify issues and improve your crawling strategy.
2. Indexing API
Google’s Indexing API allows you to directly notify Google of changes to your site. This can be useful for quickly indexing new or updated content.
3. International Targeting
If your website targets multiple countries, use hreflang tags to indicate language and regional targeting. This helps search engines serve the correct version of your page to users.
4. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Using a CDN can improve your site’s loading speed, leading to better crawling and indexing by search engines.
Monitoring and Maintaining Indexing
Once your website is properly indexed, it’s important to continuously monitor and maintain it. Regular checks can help you catch any issues early and keep your site performing well in search results.
1. Regular Audits
Conduct regular SEO audits to ensure that your site remains properly indexed. Use tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush to identify and fix any issues.
2. Monitor Search Console
Keep a close eye on your Google Search Console account. It provides valuable insights into how Google views your site and can alert you to potential problems.
3. Content Updates
Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant. Search engines prefer websites that are actively maintained and updated.
4. Backlink Monitoring
Monitor your backlink profile to ensure you are not accumulating spammy or low-quality links, which can negatively impact your indexing and rankings.
5. Technical SEO
Stay updated with the latest developments in technical SEO. Ensure your site follows best practices for speed, mobile-friendliness, and security.
Indexing and Its Impact on Business

Proper indexing can significantly impact your business’s online presence and success. Here’s how:
1. Increased Traffic
Well-indexed pages appear in search results, leading to more organic traffic and potential customers.
2. Brand Visibility
Being indexed ensures your brand is visible to search engine users, enhancing brand awareness and credibility.
3. Competitive Advantage
Proper indexing can give you a competitive edge. If your competitors’ sites are not well-indexed, you have a better chance of outranking them.
4. Revenue Growth
More visibility and traffic can lead to increased conversions and revenue. A well-indexed site is a crucial part of a successful digital marketing strategy.
Factors Affecting Indexing
Several factors can influence how well your web pages are indexed:
- Website Structure: A clear and logical structure helps search engines crawl and index your pages more efficiently. Organize your content with categories and subcategories.
- Internal Linking: Effective internal linking allows search engines to discover new pages on your site. Ensure that all important pages are linked from other relevant pages.
- Sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website. Submitting a sitemap to search engines can improve crawling and indexing.
- Robots.txt: This file tells search engines which pages they can and cannot crawl. Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to avoid blocking important pages.
- Meta Tags: Meta tags, such as title tags and meta descriptions, provide information about your pages to search engines. Use relevant keywords and write clear, descriptive meta tags.
- Content Quality: High-quality, original content is more likely to be indexed and ranked well. Avoid duplicate content, which can harm your indexing and rankings.
- Page Load Speed: Faster pages provide a better user experience and can be crawled more efficiently by search engines. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to optimize your page speed.
- Mobile Optimization: With Google’s mobile-first indexing, it’s crucial that your website performs well on mobile devices. Ensure your site is responsive and provides a good user experience on all screen sizes.
- URL Structure: Clean and descriptive URLs help search engines understand the content of your pages. Avoid using long, complex URLs with unnecessary parameters.
- HTTPS Protocol: Secure websites (those using HTTPS) are favored by search engines. Ensure your site is secure to improve both your indexing and user trust.
How to Ensure Your Website is Properly Indexed
To ensure your website is properly indexed, follow these actionable tips:
1. Create a Sitemap
A sitemap is a blueprint of your website that helps search engines find and index your pages. You can create a sitemap manually or use tools like XML Sitemap Generator. Once created, submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
2. Optimize Your Robots.txt File
Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow search engines to crawl your important pages. Avoid disallowing pages that you want to be indexed.
3. Use Internal Links Strategically
Link to important pages from other relevant pages within your site. This helps search engines discover and index new content.
4. Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. Ensure your website is mobile-friendly to improve indexing.
5. Fix Crawl Errors
Regularly check for crawl errors in Google Search Console. Fixing these errors ensures that search engines can access and index your pages without issues.
6. Update Content Regularly
Regularly updating your content keeps it fresh and relevant. Search engines favor updated content, which can improve your indexing and rankings.
7. Use Structured Data
Implementing structured data (schema markup) helps search engines understand your content better, leading to improved indexing and richer search results.
8. Avoid Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and harm your indexing and rankings. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page when necessary.
9. Improve Page Load Speed
Ensure your website loads quickly by optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify and fix issues.
10. Implement HTTPS
Switch your website to HTTPS to provide a secure connection. Search engines favor secure sites, which can improve your indexing and rankings.
Common Indexing Issues and How to Resolve Them

Even with the best practices, you might encounter some common indexing issues. Here’s how to address them:
1. Pages Not Indexed
If some of your pages are not indexed, check your robots.txt file and meta tags to ensure they are not blocking these pages. Also, verify that the pages are linked from other parts of your site.
2. Slow Crawling
If search engines are crawling your site slowly, it might be due to server issues or a lack of internal links. Improve your site’s performance and ensure all pages are well-linked.
3. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can lead to indexing issues. Use tools like Copyscape to check for duplicates and use canonical tags to specify the original version of the content.
4. Incorrect URL Parameters
URL parameters can cause indexing issues if not managed properly. Use Google Search Console to specify how URL parameters should be handled.
5. Blocked Resources
Ensure that important resources (CSS, JavaScript, images) are not blocked by your robots.txt file. Blocking these resources can prevent search engines from understanding your site’s layout and content.
6. Thin Content
Pages with little or no valuable content may not be indexed. Ensure all your pages provide meaningful information and value to users.
7. Broken Links
Regularly check for and fix broken links. Broken links can impede crawling and indexing, leading to missed pages and poor user experience.
Tools to Help with Indexing
Several tools can help you manage and monitor your website’s indexing:
- Google Search Console: This free tool provides insights into how Google is indexing your site and highlights any issues that need attention.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Similar to Google Search Console, this tool provides insights and diagnostics for Bing’s indexing of your site.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: This tool crawls your site like a search engine, providing detailed reports on your site’s structure, links, and indexing status.
- XML Sitemap Generators: Tools like XML Sitemap Generator help you create and manage sitemaps for your website.
- Copyscape: Use this tool to check for duplicate content and ensure your pages are unique.
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Use this tool to analyze and improve your site’s loading speed.
- Ahrefs: A comprehensive tool for SEO analysis, including site audits, backlink analysis, and keyword research.
- SEMrush: Another powerful SEO tool that provides insights into your site’s performance, keyword rankings, and competitor analysis.
- Moz Pro: Offers various SEO tools to help with keyword research, link building, and site audits.
In the next blog, we’ll delve deeper into advanced indexing techniques, explore emerging trends in search engine optimization (SEO), and provide actionable insights to help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving landscape of Digital Marketing. Stay tuned for an in-depth exploration of how to master indexing and drive tangible results for your business.
FAQ
1. What is indexing in digital marketing?
2. Why is indexing important for my website?
3. How can I check if my website is indexed?
.com” into the Google search bar. Google Search Console is another tool that provides insights into your website’s indexing status.




